Renaud JM, Al‑Mallah MH, Soman P, de Kemp RA, Beanlands RSB, Armstrong IS, Prior JO, Madamanchi C, Goonewardena SN, Poitrasson‑Rivière A, Moody JB, Ficaro EP, Murthy VL. How to Differentiate Obstructive from Non‑Obstructive CAD with PET: Developments in High‑Resolution Regional Quantification of MBF and MFR. Journal of Nuclear Cardiology. 2024;41:102023. Conference contribution.
Description:
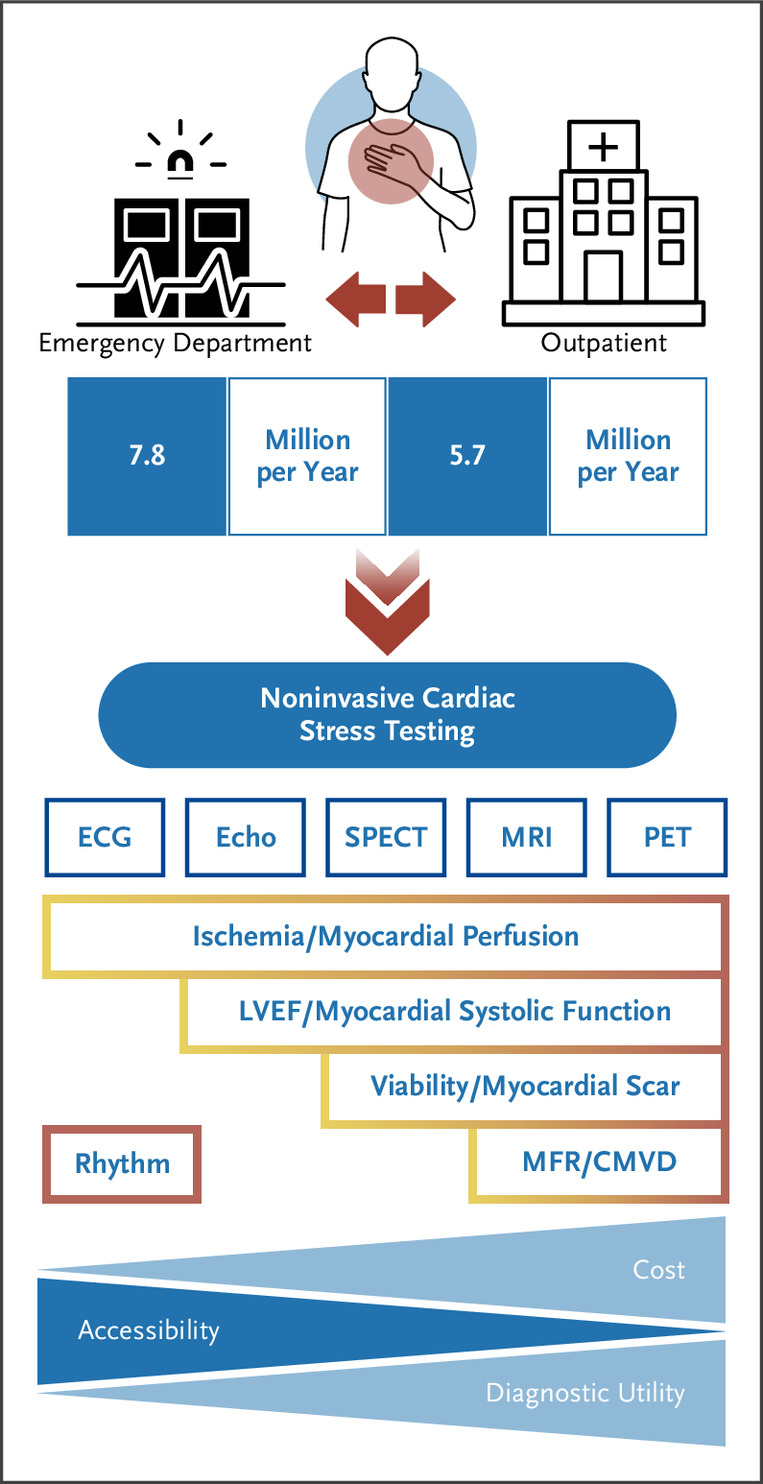
This conference abstract (published in Journal of Nuclear Cardiology, November 2024 supplement) presents advancements in high-resolution regional quantification of myocardial blood flow (MBF) and myocardial flow reserve (MFR) using PET imaging with ¹⁸F‑flurpiridaz. The work aims to improve differentiation between obstructive and non‑obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD).
The authors evaluated segmental-level MBF and MFR assessments and compared them with global and vessel-level analyses. Specific optimization techniques such as motion correction and refined temporal sampling were employed to enhance measurement precision.
Key Findings:
- Refined flow metrics: High-resolution (minimal-segment) MBF and MFR measures showed statistically higher diagnostic performance (AUC ~0.87) than vessel-based or global MBF/MFR (AUC ~0.83 and 0.77)
- Effect of motion correction / resampling: Incorporating motion correction and improved temporal framing further improved flow quantification reliability.
Clinical Relevance:
Quantification of MBF and MFR at a segmental resolution—along with motion correction and optimized sampling—may substantially improve the accuracy of PET MPI in distinguishing obstructive from non‑obstructive CAD using ¹⁸F‑flurpiridaz. This suggests greater potential value in regional PET flow metrics versus conventional global estimates.
Partners in Research:
INVIA Medical Imaging Solutions and the Houston Methodist DeBakey Heart & Vascular Center, the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, the University of Ottawa Heart Institute, Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust, University of Lausanne, Lausanne University Hospital and the University of Michigan collaborated on this research.