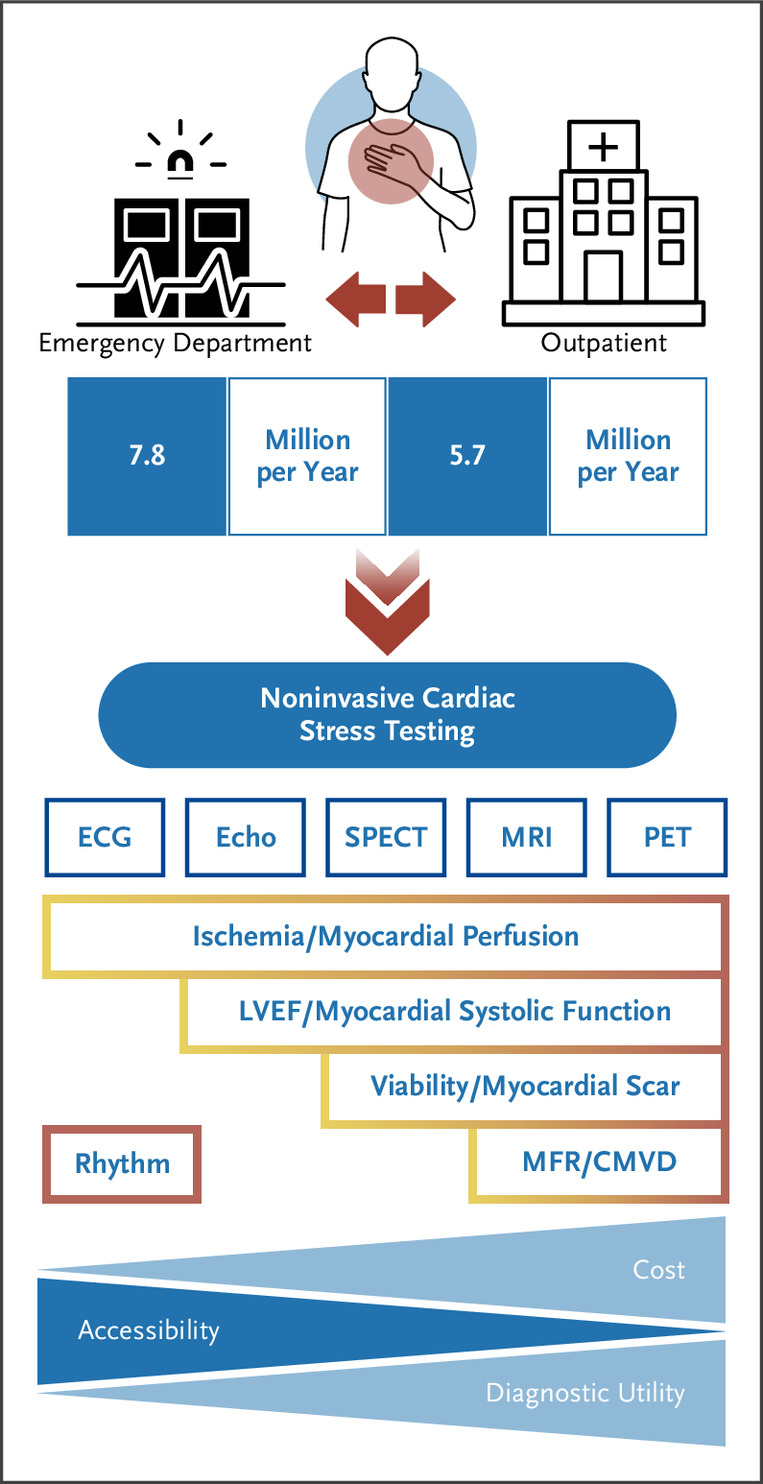
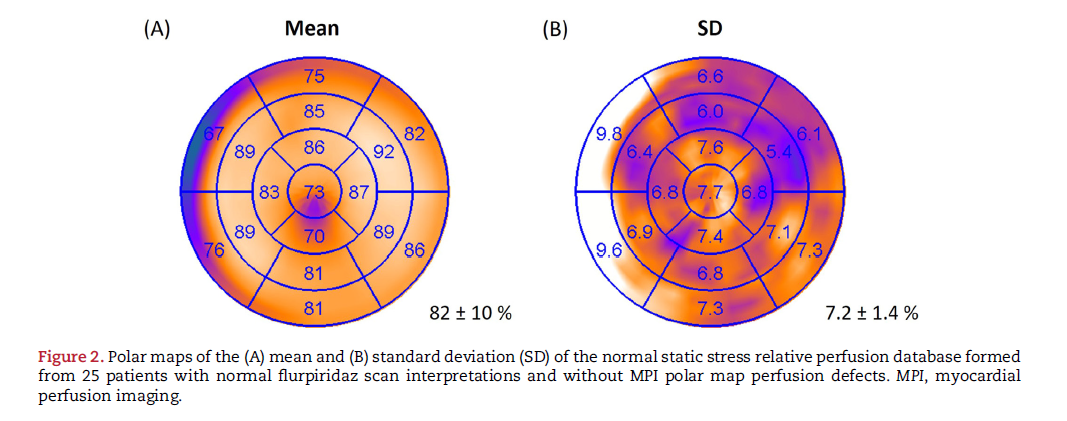
Shinn K, Hamer Y, Poitrasson‑Rivière A, et al. PYP quantification of amyloid burden in transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy and correlation with echocardiogram. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2024;83(13 Suppl). Conference abstract.
Description:
This conference abstract, appearing in the supplement to the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (April 2024), examines quantitative metrics derived from Tc-99m pyrophosphate (PYP) imaging in patients with transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy (ATTR‑CM). The study explores how quantitative measures of myocardial amyloid burden from PYP correlate with echocardiographic findings.
The analysis includes standardized uptake values (e.g., SUVₘₐₓ, SUVₘₑₐₙ) and cardiac amyloid activity metrics on PYP SPECT, and compares these to echocardiographic parameters such as wall thickness and function.
Key Findings:
- Quantitative correlation: Higher PYP-based quantitative amyloid burden measures were associated with increased ventricular wall thickness and echocardiographic abnormalities, suggesting alignment between nuclear imaging uptake and structural echo metrics
- Emerging approach: Quantification may provide more refined assessment of amyloid burden than conventional visual grading alone, though further validation is needed.
Clinical Relevance:
Quantitative PYP imaging may offer complementary insight to echocardiography in assessing cardiac amyloidosis in ATTR‑CM. These metrics could enhance early detection and tracking of disease progression, especially in contexts where echocardiographic abnormalities are subtle or evolving.
Partners in Research:
INVIA Medical Imaging Solutions and the Division of Cardiovascular Medicine in the Department of Internal Medicine at the University of Michigan collaborated on this research.