Arida-Moody, L., Moody, J.B., Renaud, J.M. et al. Effects of two patient-specific dosing protocols on measurement of myocardial blood flow with 3D 82Rb cardiac PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 48, 3835–3846 (2021).
Description:
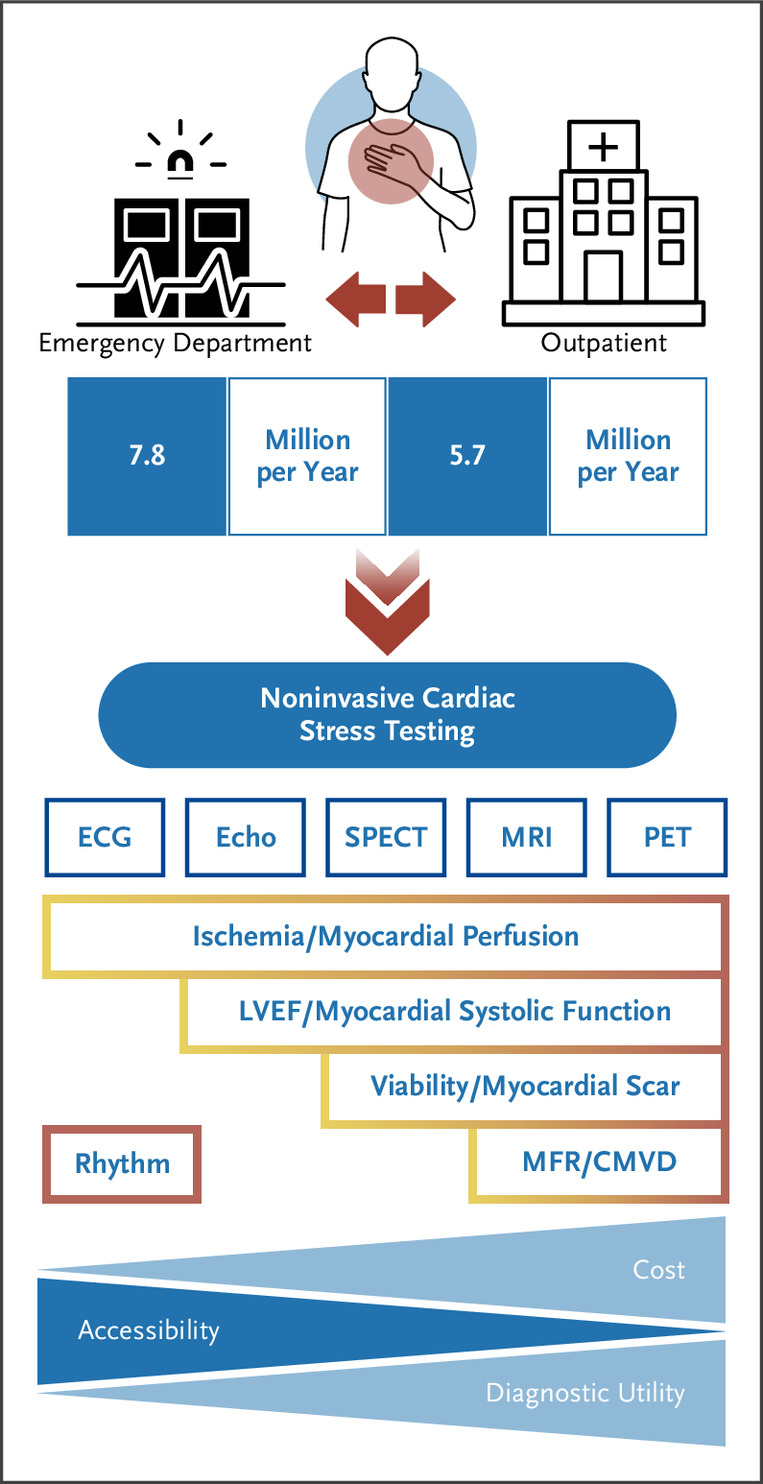
This study evaluated the efficacy of patient-specific dosing protocols, specifically weight- and BMI-adjusted dosing, for quantitative myocardial blood flow (MBF) accuracy in PET myocardial perfusion imaging.
A total of 435 patients underwent rest and stress PET-CT assessments with 82Rb activities, and the effects of the dosing protocols on dose reduction, PET scanner saturation, relative perfusion, and image quality were analyzed. BMI-adjusted dosing resulted in lower administered activities, reduced PET scanner saturation incidence and severity, and maintained image quality and relative perfusion assessment accuracy.
Clinical Relevance:
Implementing BMI-adjusted dosing in PET myocardial perfusion imaging can effectively reduce administered radiotracer doses while preserving image quality and diagnostic accuracy. This approach addresses the guideline-directed need for patient-specific dosing, minimizing radiation exposure and improving scanner performance without compromising the accuracy of MBF and myocardial flow reserve (MFR) quantification. These findings support the routine use of BMI-adjusted dosing in clinical settings to enhance patient safety and the reliability of diagnostic assessments in coronary artery disease management.

Partners in Research:
The University of Michigan, INVIA Medical Imaging Solutions, and Siemens Health collaborated on this research.